Twin Shaft Mixer Design
A twin shaft concrete mixer is a commonly used piece of equipment in construction engineering, primarily used to mix materials such as cement, sand, aggregate, and water to produce concrete. The twin shaft mixer design revolve around three core objectives: efficient mixing, uniform agitation and adaptability to different material characteristics, ensuring the equipment achieves high productivity, low energy consumption, and a long service life in concrete production.
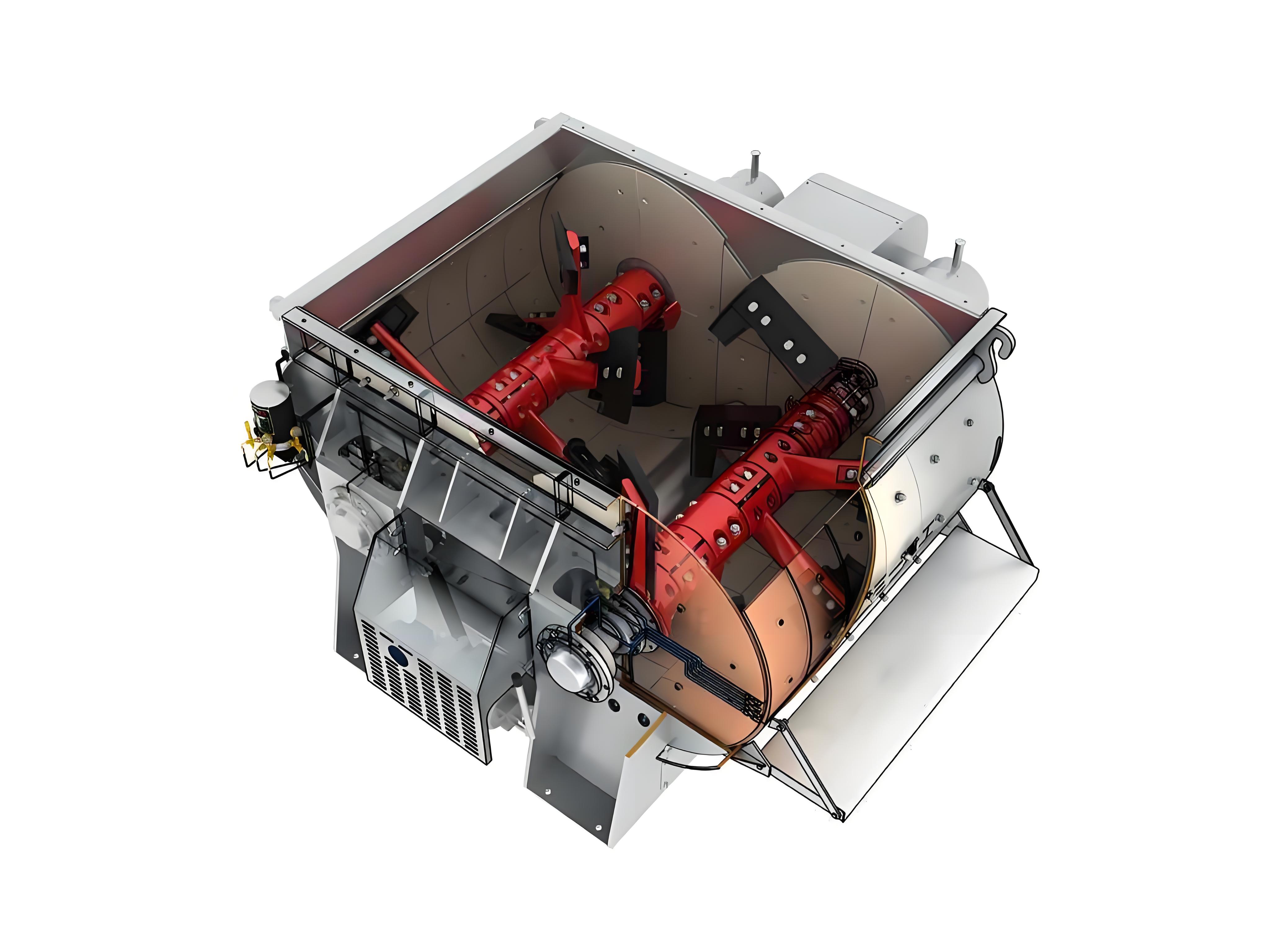
Key structural design of a twin shaft concrete mixer:
1. Mixing device
- Twin shaft structure:
Employs two horizontally parallel mixing shafts, each equipped with multiple sets of helically arranged mixing blades. The blade design must meet the following conditions:
- Opposite helical directions:
One shaft rotates clockwise, and the other counterclockwise, creating cross-flow of materials, enhancing material shearing and compression effects.
- Optimized blade angles:
Larger blade angles (e.g., 40°-45°) at the inlet and outlet ends accelerate material propulsion; smaller blade angles (e.g., 30°-35°) in the middle extend mixing time and improve uniformity.
- Blade material:
Utilizes high-wear-resistant alloy steel (e.g., 40Cr), heat-treated to more than double tensile strength, reducing the risk of breakage.
2. Mixing tank design:
- Circular groove cross-section:
Reduces material residue and improves discharge efficiency.
- Liner material:
Utilizes high-chromium alloy or hardened gear material, with a lifespan of up to 10 years, reducing wear costs.
3. Transmission system:
- Geared motor drive:
Connected to the mixing shaft via a coupling, achieving a stable speed of 47 rpm to ensure effective mixing.
- Hydraulic discharge Device:
Composed of a pump, distributor, and cylinder, controlling the opening and closing of the discharge gate for rapid discharge (≤30 seconds).
4. Frame and support:
- Welded channel steel frame:
Provides rigid support and reduces vibration.
- High-strength anchor bolts:
Fixed to a concrete foundation platform with a levelness deviation ≤2‰, preventing swaying during operation.
5. Electrical Control System:
- Integrated operation panel:
Equipped with start, jog, stop, timer, discharge, and reset buttons, supporting automated production processes.
- Safety interlock device:
Prevents equipment damage or personal injury due to misoperation.
Forced mixing working principle:
When the mixing shaft rotates, the blades apply shearing, compressive, and tumbling forces to the material, causing it to form a complex motion trajectory within the drum:
- Axial Push:
The blades push the material from one end to the other, creating cross-flow.
- Radial Tumbling:
The blades lift the material from the bottom, enhancing mixing between upper and lower layers.
- End-Face Blade Assistance:
Prevents material accumulation at the shaft ends, improving the uniformity of mixing dead zones.
Key features of twin shaft concrete mixer include:
- Twin shaft design:
The twin shaft mixer is equipped with two mixing shafts, enabling more uniform mixing and improving the quality and homogeneity of concrete.
- High efficiency mixing:
Due to the twin-shaft design, the mixing efficiency is high, suitable for large-scale production needs.
- Wide applicability:
Can be used for various types of concrete production, including ordinary concrete, high-strength concrete, and masonry mortar.
- Durability:
Mixing blades are typically made of wear-resistant materials, extending service life and reducing maintenance costs.
- Automated control:
Modern twin-shaft concrete mixers are usually equipped with automated control systems, enabling precise batching and monitoring of the mixing process, improving production efficiency.
- Easy to clean:
The design usually takes into account the ease of cleaning, making it easy to clean between different batches and avoiding cross-contamination of materials.

